中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (20): 3666-3670.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.20.008
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
线性测量颞下颌关节在咬合重建中的可适位
栾 巍1,石旭旭2
- 1佳木斯大学,黑龙江省佳木斯市 154002
2大庆油田总医院口腔修复科,黑龙江省大庆市 163001
Proper position of the temporomandibular joint in the occlusal reconstruction with linear measurement
Luan Wei1, Shi Xu-xu2
- 1 Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China
2 Department of Prosthodontics, Daqing Oilfield General Hospital, Daqing 163001, Heilongjiang Province, China
摘要:
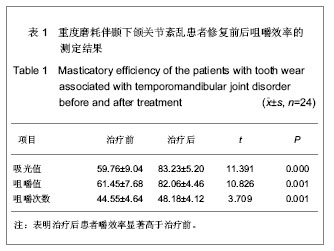
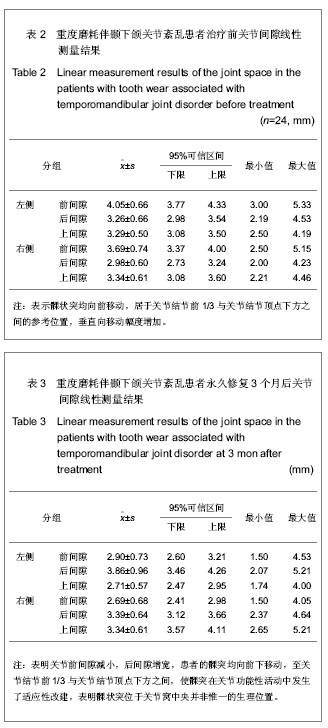
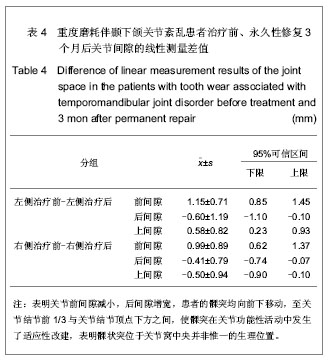
背景:牙合面形态的改变影响咀嚼肌的收缩、咬合力的大小与方向,进而影响包括颞下颌关节在内的整个口颌系统的受力环境,是颞下颌关节生理性和病理性改建的最主要的刺激因素。 目的:测量分析髁状突在咬合重建中的可适位。 方法:对24例牙列重度磨耗伴颞下颌关节紊乱患者采用固定修复方法进行咬合重建治疗,疗程9个月,治疗前后拍摄正中牙合位颞下颌关节CT片利用计算机技术进行线性测量,分析关节间隙的变化。 结果与结论:咬合重建修复治疗后髁突在关节窝内相对参考位置,左侧由-(16.96±2.01)%增至+(14.20±1.24)%;右侧为-(10.64±1.50)%增至(11.51±3.00)%。治疗前的咀嚼效率约为治疗后的62.15%-89.09%,平均为74.88%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。24例咬合重建后的患者髁状突在关节窝中均向前下移位至关节结节前1/3与关节结节顶点下方之间。提示咬合重建后髁状突向前下移位至关节结节前1/3与关节结节顶点下方之间的可适位改建取得了良好的临床治疗效果,髁状突位于关节窝中央并非惟一的生理位置。
中图分类号:
.jpg)